Cloud
https://landscape.cncf.io/
Characteristics
The NIST Definition of Cloud Computing (publication 800-145) is defined what is Cloud.
5 Essential Characteristics of the Cloud:
- On-demand self-service
- “a consumer can unilaterally provision computing capabilities… …as needed automatically without requiring human interaction with each service provider.
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- “…resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model…”
- “There is a sense of location indepedence in that the customer generally has no control or knowledge over the exact location of the provided resources…”
- Rapid elasticity
- “Capabilities can be elastically provisioned and released…to scale rapidly outward and inward commensurate with demand”
- “To the consumer, the capabilities available for provisioning often appear to be unlimited…”
- Measured service
- “Resource usage can be monitored, controled, and reported providing transparency for both the provider and consumer of the utilized service.”
Deployment Models
- Public
- Azure, AWS, Google Cloud
- Is easy
- Private
- Be very skeptical
- Hybryd
- Public + Public
- Public + Private
- Be skeptical
- Community
- It exists
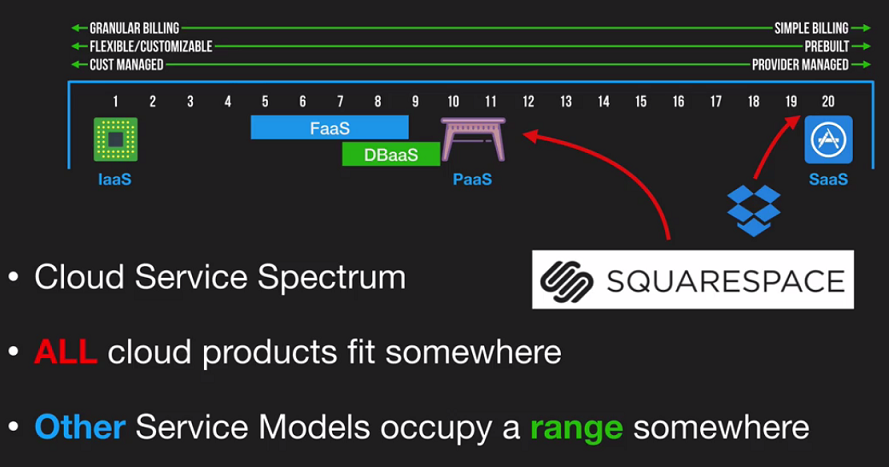
Service Models
Service model defines what end-users gets, manages, sees.
Unit of consumption (UoC) term is defined what you as a customer consume from service provider. Billing (cost) for service is based on UoC.
Three service models:
- IaaS - Infrastructure as a Service
- UoC: VM or OS
- Billing: Per second/minute/hour when VM is active
- PaaS - Platform as a Service
- UoC: Runtime Environment (Node.js, PHP, etc.)
- SaaS - Software as a Service
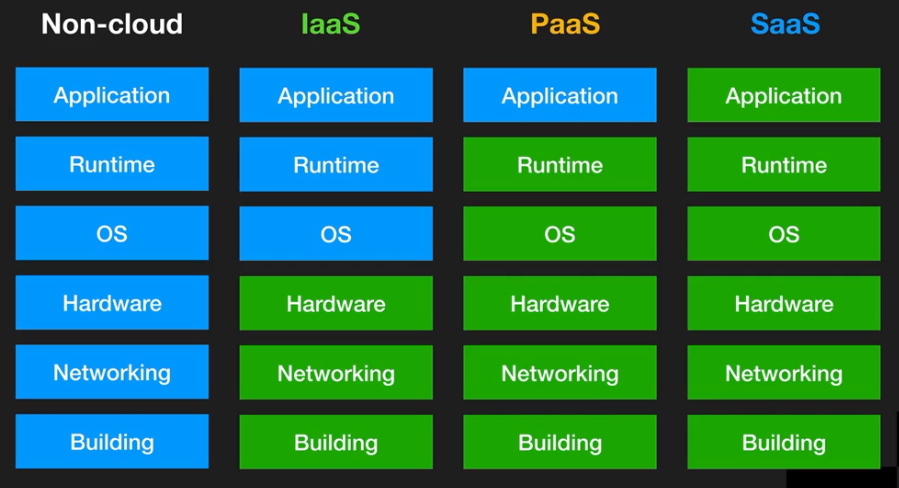
IaaS -> PaaS -> SaaS:
- You loose flexibility
- You gain in terms of easy of management: less costs, less risks
AWS and Azure service models priorities and path.
- Azure more SaaS and PaaS
- AWS more IaaS and PaaS

Additional notable service models:
- FaaS - Function as a Service - when you upload a single function (serverless architecture). Examples: Azure Functions, AWS Lambda
- DBaaS - Database as a Service. Examples: Azure Cosmos DB, AWS DynamoDB, Google Spanner. They have fairly deep into performance tuning and configuration.